Alteon's AGE crosslink agent shows promise in isolated systolic hypertension
Phase IIa study shows "significant" decrease in pulse pressure
On January 3, Alteon Inc. (Ramsey, NJ) announced results from a Phase IIa clinical trial evaluating the safety, efficacy, and pharmacology of ALT-711, a first of its kind advanced glycosylation end-product (AGE) crosslink breaker. AGE crosslinking is a natural part of aging that leads to stiffening and loss of function in tissues, organs, and vessels including large arteries.
In this study, patients taking ALT-711 experienced a statistically significant reduction in arterial pulse pressure, defined by the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressures. Also observed was a clinically relevant increase in large artery compliance, an indicator of greater vascular flexibility and volume capacity, using a traditional measurement of the ratio of stroke volume to pulse pressure. Additionally, ALT-711 was well tolerated.
Isolated systolic hypertension (ISH), defined as elevated systolic pressure above 160 mmHg accompanied by normal diastolic pressure, represents a significant unmet need—as well as an opportunity for Alteon. Affecting nearly 8 million Americans, ISH increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and death. According to Alteon, ALT-711 is the first drug to show activity against ISH by targeting stiff vessel disease that contributes to this form of hypertension.
"Currently available cardiovascular treatments do not directly target vascular stiffening and, as a result, are not optimal for the treatment of isolated systolic hypertension," said Edward G. Lakatta, chief of the Laboratory of Cardiovascular Science at The National Institute on Aging and an investigator in this study. "The ALT-711 results are exciting in that selective enhancement of large artery distensibility with reduced pressure pulsation was achieved, providing a novel approach for the treatment of isolated systolic hypertension."
Study design
Alteon's Phase IIa human clinical trial was a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study evaluating safety, efficacy, and pharmacology in 93 patients over the age of 50 with measurably stiffened cardiovasculature, including systolic blood pressure of at least 140 mmHg and pulse pressure of at least 60 mmHg. Patients were randomized to receive 56 consecutive daily oral doses of either 210 mg of ALT-711 (n=62) or placebo (n=31) during an 8-week period. During the study, which was conducted at nine U.S. clinical sites, patients were evaluated for cardiovascular elasticity and function as measured by pulse pressure, cardiovascular compliance, pulse wave velocity and cardiac output. Treatment with ALT-711 was in addition to all other medications.
Based on favorable results from this trial, Alteon plans to initiate Phase IIb efficacy trials over the next year to assess ALT-711's activity in isolated systolic hypertension as well as other therapeutic applications.
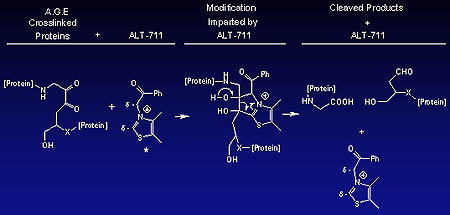
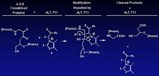
ALT-711 works by cleaving carbohydrate-protein bonds characteristic of AGE complexes.
AGE crosslink breakers
Advanced glycosylation end-products are permanent glucose structures that form when glucose binds to the surface of proteins. These structures interact with adjacent proteins to form pathological links called AGE crosslinks. Diabetics form excessive amounts of AGEs earlier in life than non-diabetics, and therefore show increased stiffness of tissues, abnormal protein accumulation, and organ dysfunction—events that underlie many of the complications of aging and diabetes. In the cardiovascular system, loss of vasculature flexibility leads to ISH, which in turn may result in an enlarged heart and heart failure.
Alteon has created a library of novel agents that work on the AGE pathway, including AGE crosslink breakers, AGE formation inhibitors, and glucose lowering agents.
For more information, contact Susan M. Pietropaolo, director of investor relations for Alteon Inc., at 201-818-5537.
With contribution from Angelo DePalma
Managing Editor, Drug Discovery Online and Pharmaceutical Online
Email: adepalma@vertical.net
