A Brief Overview Of Epigenetics
By Ranjana Jain, Research Nester

The term “epigenetics” was first coined in 1942 by the famous British embryologist Conrad Waddington. Epigenetics is an emerging domain of scientific research that studies how the environment and behaviors can cause changes that affect the way genes work. Here, epi means above or on in Greek, and “epigenetic” defines the factors beyond the genetic code. Epigenetic changes do not alter the DNA sequence and are reversible. However, they are able to change how the body reads a DNA sequence. It is the study of how cells control the activity of genes.
The human body is thought to have about 1 million genes, and a total of around 100 million nucleotide pairs of coding DNA are calculated to be available in the human genome. These genes play an imperative role in defining your health status, along with your environment and behaviors, such as, for example, what you eat and how physically active you are. For example, behavioral changes such as dieting and exercising can result in epigenetic transformation. It is very useful to witness a connection between behaviors, genes, and the environment.
Epigenetics can be used to help determine the type of cancer a person may have and to discover the cancer at earlier stages. Epigenetic drugs are highly potent and capable of reversing gene expression. Scientific researchers believe that epigenetics are moving toward a “paradigm shift” in various domains of medical and biological research.
The 3 Common Types Of Epigenetic Modification
1. DNA Methylation
The human genome consists of 24 different DNA molecules, and a complete human gene map consists of 24 maps. DNA methylation is a process in which the modification is achieved by putting chemicals into the DNA. The chemicals are added to particular places on the DNA where they block the protein that is associated with the DNA, changing how the gene is read.
Furthermore, demethylation is the process by which chemical groups can be eradicated. Hence, it can be concluded that demethylation turns a gene on and methylation turns the gene off.
2. Histone Modification
Histones are a group of globular proteins having a high content of lysine and arginine amino acids. In the eukaryote, histones fabricate part of the chromosomal material. The histone proteins, which are categorized into five different types, are shown below:
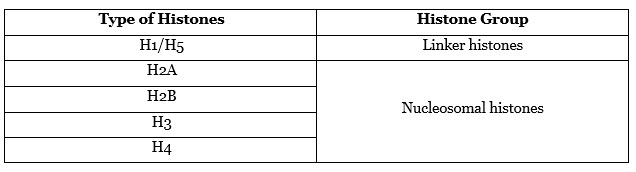
Here, the H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 occur in pairs to generate the core of the nucleosome. The function of the histones is to provide a medium around which DNA is wrapped around. Moreover, they play a crucial role in gene regulation.
When histones are packed tightly, the protein that reads the gene becomes unable to access the DNA easily, and hence the gene gets turned off. On the other hand, when the histones are loosely packed, a substantial amount of DNA is exposed, or not wrapped around the histones, so the gene is turned on.
3. Non-coding RNA
DNA is utilized as instructions for fabricating non-coding and coding RNA. Coding RNA is used to develop proteins, while non-coding RNA helps control gene expression. The non-coding RNA recruits proteins to make advancements in the histones to turn genes off or on.
The Current And Future Outlook
The epigenetics market was valued at $1.5 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to reach $4.2 billion by 2030. Factors driving this market growth include:
- an increase in the incidences of infectious diseases, cancer, chronic conditions, and genetic conditions;
- rising spending on healthcare, which, according to the American Medical Association, registered over $187.6 billion in 2021; and
- the growing interest in bioinformatics, the market for which reached $10 billion in revenue in 2022.
Some of the key market players are: Abcam Plc, Active Motif, Agilent Technologies, Hologic, Illumina, Merck Millipore, PerkinElmer, QIAGEN NV, and Thermo Fisher.
Scientists are exploring the relationships between chemical compounds and the genome in order to modify gene expression. The sector holds a wealth of opportunities as we move into the future.
Suggestions For Further Reading
- Approval of First ‘Epigenetic’ Drug for a Solid Tumor is Milestone (via Dana-Farber Cancer Institute)
- Advances in epigenetic therapeutics with focus on solid tumors (via Clinical Epigenetics)
- Novel Approaches to Epigenetic Therapies: From Drug Combinations to Epigenetic Editing (via Genes [Basel])
- Role of epigenetic drugs in sensitizing cancers to anticancer therapies: emerging trends and clinical advancements (via Epigenomics)
- Omega Therapeutics’ Approach To Epigenetics (via Cell&Gene)
